|
Molspec-ID Online Database (MSDB) 1.0 |


|
| Home |
| Database |
|---|
| Overview |
| Taxonomies |
| PCR |
| Primers |
| Sequences |
| Genetic Elements |
| Publications |
| Organisations |
| Persons |
| The Project |
|---|
| Project Intro |
| Docs & Publications |
| Slides & Meetings |
| [ Work Packages ] |
| Partners |
| Contact |
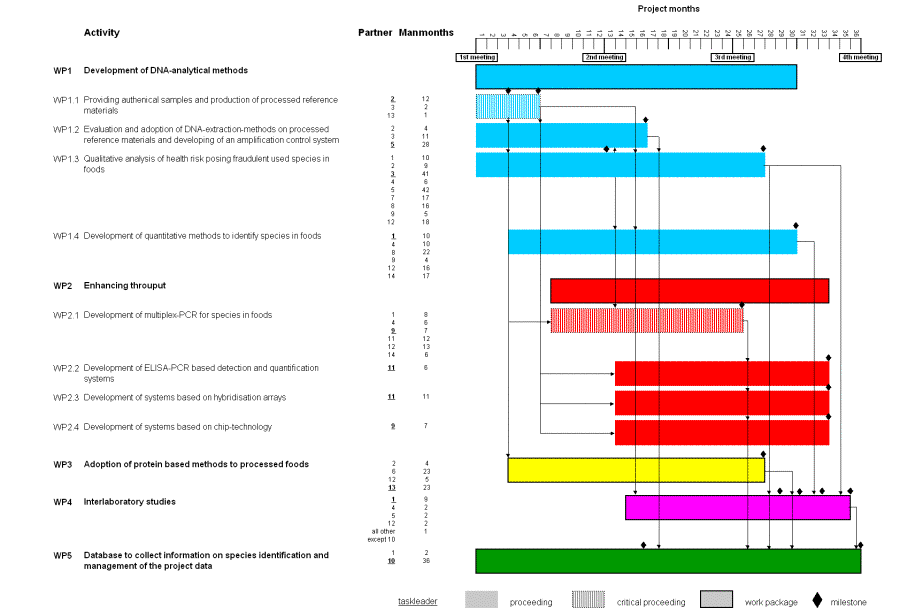
Work Packages
of the MOLSPEC-ID project
Connection and Description | Scheduling | WP1 | WP2 | WP3 | WP4 | WP5
Connection of the Work packages
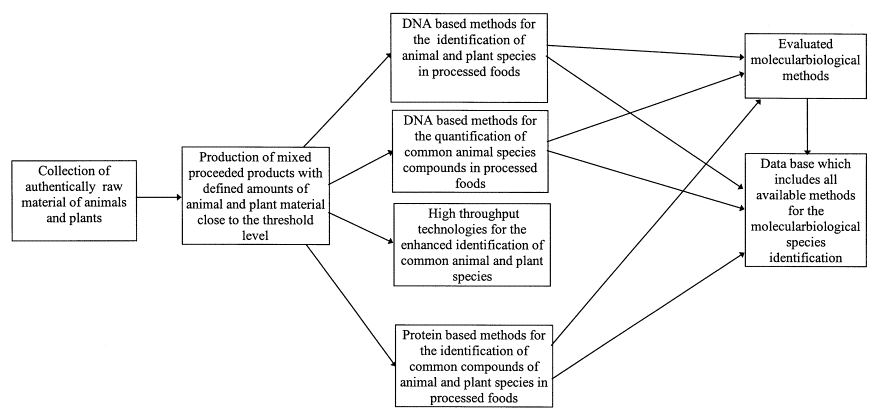
| Work package name: | Description: |
| WP1: DNA-based methods | In WP 1 detection methods for several plant and animal species (Tab. 1) based on qualitative and quantitative PCR will be developed. WP 1 consists of the following tasks:
|
| WP2: Enhancing | In WP 2 the aspect of enhancing throughput is covered. This will be achieved by the development of multiplex PCR systems followed by the development of systems which will be suited to screen for a greater panel of species in parallel. WP 2 consists of the following parts:
|
| WP3: Protein based methods |
The basis of WP 3 will be the evaluation of protein based methods for several species. With selected samples the efficiency of DNA- in comparison with protein-analytical methods will be studied. |
| WP4: Interlabotatory studies | In WP 4 four interlaboratory studies for the evaluation of developed methods should be realised. The methods will be evaluated in ring trails with project partners and external guests. |
| WP5: Database | In WP 5 a database will be set up which shall comprise information about the extraction and detection systems. It should collect information on species identification and management of the project data. |
Work package [WP] 1:
In WP 1 detection methods for several plant and animal species (Tab. 1) based on qualitative and quantitative PCR will be developed. WP 1 consists of the following tasks:
WP 1.1: The providing of authentical samples and the production of processed reference materials (sausages and canned products).
WP 1.2: Evaluation and adoption of DNA-extraction methods on processed reference materials. An amplification control system should be developed.
WP 1.3: Qualitative analysis of health risk posing species and qualitative analysis of fraudulent used species in food products.
WP 1.4: Development of quantitative methods to identify species in foods.
WP 1.1. Providing authentical samples and production of processed reference materials
December 2001-Mai 2002
Technical Objectives: This work package will provide processed food samples with defined amounts of species as well as authentic raw materials for qualitative analysis. Processed products under investigation will be: sausages and tins containing different percentages and combinations of beef, pork, sheep, chicken, duck, turkey, horse. Furthermore hamburger with beef, chicken, pork , lamb and horse, liver paté (from beef and pork) containing chicken and turkey and surimi-based fish products (with or without crab meat). The spectra of samples of exotic species and species of regional interest will include deer, bovid species, ostrich and kangaroo and others. Furthermore the BgVV will provide authentic food samples (e.g. goulash, jellied meat) containing defined amounts of soybean as well as pig, beef, lamb, chicken, turkey.
Task leader: 2
Inputs: Experience of partner 2
Outputs: Prototype reference materials suited to study a minimum of 1 % of a given species will be made available for quantitative studies and ring trials. The sample preparation is a prerequisite for further work. Principal feedback and information about reference materials on the field of species quantification is to be expected. Recommendations on sample preparation will be available at the end of the project.
WP 1.2. Evaluation and adoption of DNA-extraction methods on processed reference materials and developing of an amplification control system
Time Schedule: December 2001-April 2003
Technical Objectives: DNA extraction methods will be collected and optimised for raw materials and samples prepared in WP 1.1. Methods will be based on available literature or former projects that have not been applied to samples of WP 1.1 before. The methods include the use of commercially available kits as well as modified CTAB-protocols or combinations of both. Partners will provide their results gained from other work packages in which they are involved. DNA isolation is the most critical step in development of PCR based methods. Therefore internal standards of approximately 100 bp in length will be developed for use in amplification assays to monitor DNA quality.
Task leader: 5
Inputs: Experience of partners and existing methods, products of WP 1.1
Outputs: A detailed description of suitable methods will be available after the projects end and will be made public via a database (see below). WP 1.2 starts in parallel with WP 1.3. At the end of the work package WP 1.2 results will be integrated into the data base (see WP 5). Limits of DNA isolation methods depending from the processing stage of the food samples will be determined.
WP 1.3. Qualitative analysis of health risk posing species and analysis of fraudulently used species in food products
Time Schedule: December 2001-March 2004
Qualitative methods will be developed for the unambiguous identification of trace amounts of species that are known to bear potential health risks and/or used for fraudulent replacement in processed foods. The following plant ingredients will be studied: nuts (hazelnut, almond, walnut), Leguminosae (soybean, peanut), four gluten-containing cereals (wheat, barley, oat, rye). The following food of animal origin playing a role as hidden allergen will be studied: surimi-based products composed of different fish species with or without crab meat. Crab meat will be investigated in parallel in WP 3 (Protein based methods) to render possible a comparison of efficiencies. The following non domestic species will be investigated: deer, ostrich, kangaroo and others made available by partners. Methods will be a) Developing and testing of primer pairs for PCR with subsequent confirmation of amplicons by either enzymatic restriction analysis, hybridisation with specific probes or sequencing; b) Developing of species-specific markers by analysis of primarily microsatellites. Sources used in system development will be sequence and literature databases.
Task Leader: 3
Other participants: 1, 2, 4, 5, 7, 8, 9, 12
Inputs: Experience of partners and existing databases and literature.
Outputs: The results will be collected in a public report at the end of the project. At least one selected method will be evaluated in a ring trial with members of the project. The results of this may serve as a basis for an official method in the European member states. Newly developed PCR systems will be made public via the database established in WP 5. Methods will be made available for at least three different species of nuts, four cereal species and crab meat in processed products after two-third of the project. The knowledge will be extended by the appropriateness of existing methods. The comparison of results derived from WP 1.3 with WP 3 will help to judge the suitability of methods for different processed foodstuffs.
WP 1.4. Development of quantitative methods to identify species in foods
February 2002-Mai 2004
Technical Objectives: The aim of this work package is the development of quantitative PCR-based detection methods to analyse components playing a role in fraud. For the following species a quantitative method will be developed: pig, cattle, lamb, turkey, chicken, duck, horse, soybean and pea. Methods employed will be based on real-time analysis of PCR products (e.g. TaqMan- and Fluorescent Resonance Energy Transfer Technology, FRET).
Task leader: 1
Other participants: 4, 8, 9, 12, 14
Inputs: Experience of partners and developed methods of WP 1.2, 1.3, 1.4 and products of WP 1.1
Outputs: The results will be collected in a public report at the end of the project. At least one selected method will be evaluated in a ring trial with members of the project. The results of this may serve as a basis for an official method in the European member states. Newly developed PCR systems will be fed into the database established in WP 5. For all species mentioned above, quantitative methods will be worked out. Due to the evaluation of at least one quantitative method the reliability of this approach will be estimated. The experiences of this work package may support the development of further quantitative methods for food quality control.
Workpackage 2:
In WP 2 the aspect of enhancing throughput is covered. This will be achieved by the development of multiplex PCR systems followed by the development of systems which will be suited to screen for a greater panel of species in parallel. WP 2 consists of the following parts:
WP 2.1: Development of multiplex-PCR for species in foods
WP 2.2: Development of ELISA-PCR based detection and quantification systems
WP 2.3: Development of systems based on hybridisation arrays
WP 2.4:Development of systems based on chip-technology
WP 2.1. Development of multiplex-PCR for species in foods
Time Schedule: June 2002-January 2003
Technical Objectives: The aim of this work package is to enhance the efficiency of analysis of species which commonly occur mixed up in complex foods (e.g. different types of meats). Based on the PCR systems developed in WP1.3 and 1.4 multiplex PCR systems for different panels of species in one assay will be developed and verified with reference materials. Detection limits of the single components will be estimated.
Task leader: 9
Other participants: 1, 4, 11, 12, 14
Inputs: Experience of partners and developed methods of WP 1.3 - 1.4.
Outputs: The results will be collected in a public report at the end of the project. The results serve as a basis for the development of chip-technology in WP 2.2. Primer systems will be made public via the database in WP 5. The analysis of several components in parallel shall be made possible to enhance the throughput in qualitative sample investigation.
WP 2.2. Development of ELISA-PCR based detection and quantification systems
Time Schedule: January 2003-September 2004
Technical Objectives: The aim of this work package is the development of ELISA-PCR based systems which enable moderate to high throughput species detection and quantification The ELISA-PCR technology is undergoing a rapid developmental stage with a fast growing number of users. The technology allows not only a qualitative analysis but also, in conjunction with existing software, a quantification of the PCR product. The attractiveness of ELISA-PCR lies on the combination of an extremely sensitive and universal technique (PCR) and a well established procedure (ELISA) based on instrumentation readily available in many laboratories already involved in food analyses with conventional antigen-antibody ELISA. Furthermore, the existing standard 96 well format allows a moderate to high throughput processing of probes.
Partner: 11
Other participants: none
Inputs: Experience of partner 9 and developed methods of WP 2.1.
Outputs: In WP 2.2 ELISA-PCR formats on the basis of the species specific single and multiplex PCR systems from WP 2.1 will be developed and it will be tested if the existing consensus systems for species identification and quantification can be adapted to standardised ELISA-PCR ready- to-use kits. Using the reference material with defined processing degrees and species composition the sensitivity of the ELISA-PCR technology will be demonstrated.
WP 2.3. Development of systems based on hybridisation arrays
Time Schedule: January 2003-September 2004
Technical Objectives: The aim of this work package is the development of hybridisation array systems which enable the simultaneous identification of a broad panel of species. Hybridisation array techniques based on the application of dozens to hundreds of specific DNA sequences on an activated solid phase belongs to the most promising technologies for the analyses of high numbers of PCR targets. An interesting feature of this technology is its versatility. The application of the specific DNA probes can be carried out either manually or by computer driven micro application devices, resulting in variable sized hybridisation arrays without loss of resolution. Furthermore, virtually all known detection procedures can be used in conjunction with solid phase hybridisation arrays, circumventing the necessity of a specific detection instrumentation. Since the production of hybridisation arrays does not necessarily require sophisticated application devices there are no limitations on the production unit numbers. This technology allows the production of customised arrays as well as standardised ready-to-use kits.
Partner: 11
Other participants: none
Inputs: Experience of partner 11 and developed methods of WP 2.1
Outputs: In WP 2.3 Hybridisation arrays on the basis of the species specific single or multiplex PCR systems from WP 2.1 will be developed and it will be tested if the existing consensus systems for species identification can be adapted to the array format. Using the reference material with defined processing degrees and species composition the sensitivity and versatility of hybridisation arrays will be demonstrated.
WP 2.4. Development of systems based on chip-technology
Time Schedule: January 2003-September 2004
Technical Objectives: The aim of this work package is the development of chip-based systems which enable the simultaneous identification of a broad panel of species. Chip-technology is one of the most updated techniques in the analytic of DNA. On the surface of a chip some tens to hundreds of dots with biomolecules (DNA probes) can be coupled (the diameter of such dots is 40-150 Ám). These immobilised probes define an array which comprises the sensitive centre of the chip. After hybridisation of this probe array with PCR amplified and fluorescence labelled target DNA imaging of PCR products gets possible. The extreme miniaturisation and parallelisation allows simultaneously performing of different analysis. When applied in the analytical fields of foodstuffs chips are successful tools to obtain quick successful results.
Partner: 9
Other participants: none
Inputs: Experience of partner 9 and developed methods of WP 2.1.
Outputs: In WP 2.4 chips on the basis of the species specific multiplex PCR systems from WP 2.1 will be developed and it will be tested if the existing consensus systems for species identification can be adapted to the chip format. Using the reference material with defined processing degrees and species composition the sensitivity of the chip technology will be demonstrated.
WP 3. Adoption of protein based methods
The basis of WP 3 will be the evaluation of protein based methods for several species. With selected samples the efficiency of DNA- in comparison with protein-analytical methods will be studied.
Time Schedule: February 2002-February 2004
Technical Objectives: The aim of this work package is to develop immunological detection systems and to adopt existing systems on processed foods. The established methods will be compared with DNA-based methods of WP 1.3 and 1.4. As a prerequisite protein must be isolated from the complex food matrices. The further analysis includes the use of specific antibodies made available by partners to perform immunological techniques (e.g. ELISA, Western-blot). Additionally a specific antibody will be raised against crab meat in surimi products.
Task leader: 13
Inputs: Experience of partner 13 and commercial products.Outputs: The results will be collected in a public report at the end of the project. At least one selected method will be evaluated in a ring trial with members of the project. Establishment of immunological methods to detect species in processed foods. Additionally, the comparison with DNA-based methods will elucidate the applicability of both methods in different processed foods. Furthermore, the results will be fed into database of WP 5.
WP 4. Interlaboratory studies
In WP 4 four interlaboratory studies for the evaluation of developed methods should be realised. The methods will be evaluated in ring trails with project partners and external guests.
Time Schedule: January 2003-December 2004
Technical Objectives: The developed molecular biological methods of WP 1.3 and 1.4 and 3 will be validated in four ring trials To validate the developed methods of the working package 1.3, 1.4 and 3 a selection of methods will be done, which are suitable for ringtesting. The organisation of the ring trials includes the procurement and partitioning of reagents and coding of the samples. After the preparation of a working plan for the participants the reagents and the samples will be distributed among the partners. The results of the laboratories will be collected, evaluated and discussed in a final meeting.
Task leader: 1
Other participants: 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 11, 12, 13, 14
Inputs: Experience of partner 1 and the developed methods of WP 1.3, 1.4 and 3.
Outputs: A detailed description of validated methods will be available after the interlaboratory studies end and will made public via a database (see below).
Collection of the received results of all partners in a working package to a standard operation procedure (SOP) of this method.
Carrying out four ring trials with the developed methods of the WP 1.3, 1.4 and 3.
Evaluation of the results
WP 5. Database to collect information on species identification and management of the project data
In WP 5 a database will be set up which shall comprise information about the extraction and detection systems.
Time Schedule: December 2001-December 2004
Technical Objectives: Development
of an database to collect information on species identification
as a tool to co-ordinate the work of the project partners and the
ring trials.
Analysis of the needs and requirements
of the project partners and the public.
Development of a long-term data structure for information about
detection methods and organisational data.
Development of a conceptual schema
for information storage.
Extraction of a database management
system (DBMS) specific logical schema from the conceptual schema.
Implementation of a logical schema
and an on-line database for a specific software system.
Design of transaction applications
for the database, such as the user interface on the web-browser,
forms for the main queries or output-lists for publications.
Training of the project partners
in the handling of the database.
Task leader: 10
Other participants: 1
Inputs: The results of all work packages as well as data of existing methods will be included into the database.
Outputs: A database with all
information on species identification will be available for all
partners and the public.
Development of the database structure.
Possibly it has to be compatible with databases already existing
for detection methods.
Input of scientific information
on existing and new developed detection methods e.g. for PCR genetic
elements, sequences, primers, detection methods, samples and extraction
methods. For protein based methods adequate details will be collected.
Information on the taxonomy of organisms,
foodstuffs, processing procedures, sample information and administrative
information like literature, addresses, meetings, publications also
will be included into the database.
Writing of an user-manual to instruct
in the handling of the database.
© Copyright MolSpec
Disclaimer: MolSpec is not responsible for linked contents.